Lungworm: Diagnosis and Prevention
A Reduced Threat This Year, But Vaccination Remains Crucial
Published on: Feb 27, 2023
Fewer Cases Due to Weather
Good news for cattle farmers! Lungworm cases have been uncommon this year, likely due to the extended dry summer followed by a mild autumn. However, a recent report from the South West of England suggests a potential decrease in the effectiveness of eprinomectin, a common lungworm treatment. This emphasizes the importance of vaccination as a preventative measure.
Signs of Lungworm Infection
- Persistent coughing throughout the herd
- Increased breathing rate
- Difficulty breathing
- Weight loss
- Reduced milk production in lactating cows
- In severe cases, cattle may become lethargic, stand with their head down and neck outstretched.
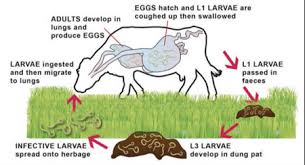
Lungworm Life Cycle
- Cattle ingest lungworm larvae while grazing.
- Larvae migrate to the lungs, mature, and reproduce.
- Eggs are coughed up, swallowed, and hatch in the stomach.
- New larvae develop and are passed in feces.
- Larvae mature on pasture and become infectious.
Diagnosis and Treatment
- Microscopic examination of feces for larvae confirms lungworm infection.
- Early treatment is crucial, as severely affected animals may not respond.
- Dead or dying larvae can worsen symptoms by blocking airways.
Who’s Most at Risk?
- Calves in their first grazing season, especially dairy calves and autumn-born suckler calves.
- Risk factors include lack of prior exposure, wet summers, and high stocking densities.
Prevention with Vaccination
- Huskvac vaccine provides protection.
- Two 25ml oral doses, four weeks apart, are given to healthy calves over 8 weeks old.
- Vaccination should be completed two weeks before turnout.
- Immunity is typically maintained through seasonal exposure to larvae on pastures.
- If grazing practices limit exposure (e.g., extensive anthelmintic use, clean pastures), a booster dose of Huskvac is recommended before turnout.
By being aware of the signs and risk factors, and prioritizing vaccination, cattle farmers can effectively protect their herds from lungworm.

Author –
Anna Hewison
Fewer lungworm cases in cattle this year, but possible decrease in treatment effectiveness identified. Learn about lungworm signs, risk factors, & the importance of Huskvac vaccination.
lungworm in cattle | cattle lungworm treatment | lungworm in calves | lungworm symptoms in cattle | lungworm life cycle | lungworm diagnosis | Huskvac vaccine for cattle | lungworm risk factors | cattle vaccination schedule | Shepton Vets cattle health











